
A woman on a smartphone reaching out of the phone to push the camera button
Photo by Designecologist from PexelsA Chinese ad network named Mintegral is accused of spying on user activity and committing ad fraud in more than 1,200 apps with 300 million installs per month since July 2019. Mintegral is headquartered in Beijing, China, and is owned by another Chinese ad network, Mobvista, which has a head office in Guangzhou, China.
One of the apps, Helix Jump, has over 500 million total installs. Other popular apps that are impacted include Talking Tom, PicsArt, Subway Surfers and Gardenscapes.
All together, this likely impacts billions of total app installs on iPhone and iPad.
There’s no exact number on how many devices or iPhone users are impacted, but Snyk says this is a “major privacy concern to hundreds of millions of consumers.”
“We identified an SDK malicious component that is getting integrated into different iOS applications and getting into the App Store,” says Danny Grander, cofounder and chief security officer at Snyk, the security company that found the issues. “That SDK is distributed as a regular ad network ... something that developers can use to monetize their apps through ads.”
Snyk notified Apple of the malicious SDK (a software component that developers use to add functionality to their apps without having to write code themselves) a week ago.
Along with standard and completely kosher ad network functionality, the Mintegral SDK performs click attribution fraud, Grander told me in an interview for the TechFirst podcast.
To do so, it also spies on user activity inside apps that have integrated it.
“Developers can sign up as publishers and download the SDK from the Mintegral site,” Snyk says. “Once loaded, the SDK injects code into standard iOS functions within the application that execute when the application opens a URL, including App Store links, from within the app. This gives the SDK access to a significant amount of data and even potentially private user information. The SDK also specifically examines these open URL events to determine if a competitor’s ad network SDK was the source of the activity.”
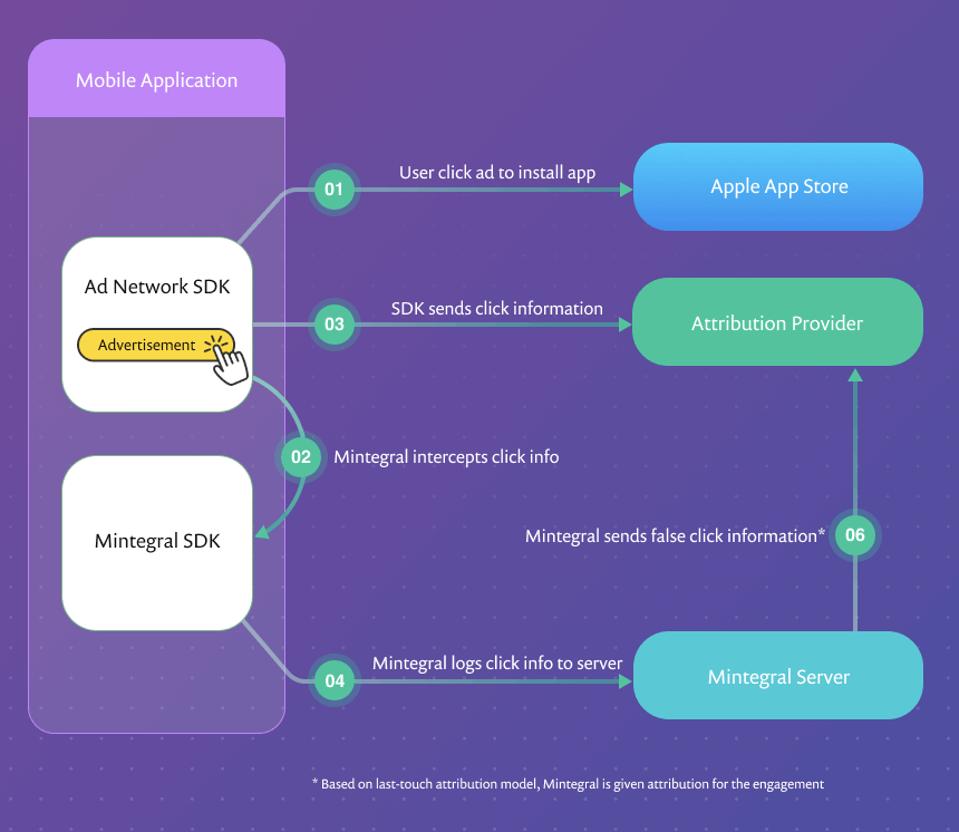
Functional flow of a user ad click being hijacked by the Mintegral SDK
SnykApparently the primary purpose of the SDK was making money. To do so it spies on what users do, including when they clicked on ads to install other apps. Since brands pay ad networks for successful mobile app installs, the Mintegral SDK would then quickly send out a fake click and “claim credit” for the app install, Grander says.
While Grander would not speculate on the total sum of stolen advertising money involved, given the scope and length of time the SDK was in operation before being discovered — over a year now — it could be in the hundreds of millions of dollars.
That’s a major issue for the advertising ecosystem.
According to advertising experts I’ve chatted with such as Eric Seufert (former VP of user acquisition for Rovio, which makes the Angry Birds apps) and Allison Schiff (an editor at AdExchanger), this kind of click injection ad fraud is fairly unique on iOS.
It’s been known on Android for some time, but it’s not common on iOS.
The bigger question for many is likely potential user privacy violations. The good news: because iOS apps are sandboxed by the mobile operating system, the SDK couldn’t go poking around for all of your information.
The bad news is that it could snoop on communication from impacted apps.
“So all the traffic that goes out of that app, they can actually instrument an intercept,” Grander told me. “Some apps would have secrets like chat, text messages, right? Other apps might have just [have] the number of coins you have won in some game.”
Snyk says that the Mintegral SDK could intercept “all HTTP requests” from apps it was integrated into. It also listened in on clicks or “URL opens,” as well as any App Store events, which of course is how it allegedly made money for its makers.
Most of the big apps are games, and there’s unlikely to be a lot of private data in games. But one, Topface, is a dating and chat app. That could have very private data. Another, Lust Puzzle, allegedly helps you “find the girlfriend of your dreams.” Meet24 is another dating app that was impacted.
According to Snyk, data collected and logged includes:
- OS Version
- IP Address
- charging state
- Mintegral SDK Version
- network type
- model
- package name
- IDFA
- URL
- request headers
- method name
- class Name
- backtrace data
Interestingly, even bad guys have bugs in their code. One piece of the SDK code was trying to capture the full body of HTTP requests (which include both a “header” and a “body”) but failed:
“The functionality of leaking the body is there, but it seems like they have some sort of bug there and so it wasn't actually doing that,” Grander says.
The fraudulent activity was well-concealed, Snyk says.
The fraudulent activity turned off if the SDK saw that it was running in a simulator, or if there was a debugger attached, or if the phone was rooted (had an unapproved operating system running), or if proxying (routing communications through a VPN or other system) was enabled.
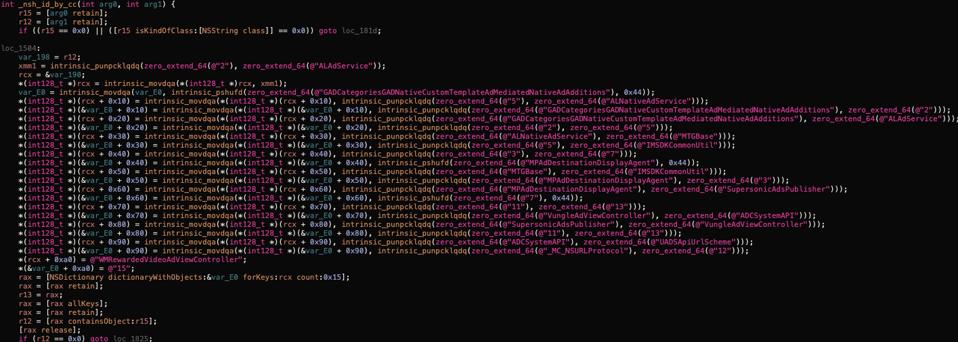
The Mintegral SDK includes code that seems to be responsible for identifying competitor SDKs, Snyk ... [+]
SnykAlso, the code that runs the exploits was obfuscated, which is likely one of the reasons why Apple did not catch the SDK during the App Store review process.
An Apple representative confirmed that the company has spoken to Snyk and provided some insight on the issue on background. Apple says that it takes user privacy extremely seriously, and there is currently no evidence that users have been harmed. In addition, however, Apple cited this as an example of why developers need to be careful about which SDKs they use, because any code an SDK uses is in their app, and any potential security or privacy misdeeds can undermine trust in their apps.
Furthermore, Apple says this is an example of why the company is making privacy enhancements in the soon-to-arrive iOS 14, which will make the Apple identifier for advertisers (IDFA) opt-in only. iOS 14 will also show people more details about what data apps are collecting.
Very likely, Apple will be tightening its own app and SDK checking in the app approval stage as well, although the Apple representative did not mention that.
With regard to the ad fraud, I talked to a mobile measurement vendor which checked for evidence of the fraud given this new information from Snyk. (Full disclosure, I do some consulting in the sector.) The vendor found that for between 20% and 30% of the conversions Mintegral had been credited with, there was a prior click within a couple minutes from a competing ad network.
That’s evidence that the Mintegral SDK could have been watching for clicks from competing ad networks and in some cases then sent a fake click afterwards.
It’s also evidence of some level of discretion in the people running the fake clicks. They didn’t try to make a huge amount of money immediately by turning it on for 100% of the ad clicks they detected, which would have resulted in much quicker discovery by ad fraud specialists. Instead, they kept it at a lower level, which would basically act as a little extra profit on top of normal business operations.
One particularly challenging component: Mintegral was integrated with a variety of mediation platforms.
Mediation platforms are kind of like a Swiss Army knife of advertising. If you want to monetize your app via advertising, you don’t want to just add one ad network’s SDK in your app: you want more options so you make the most possible amount of revenue. But you also don’t want to integrate dozens of ad network SDKs into your app. That’s a lot of work, and it makes your app bigger and potentially slower. So you use a mediation network, which integrates multiple ad network SDKs for you. Mintegral was in several, including MoPub (owned by Twitter), broadening its reach.
As mentioned earlier in this story, Snyk briefed Apple on the ad fraud SDK and its privacy implications a week ago. There’s no word yet on what Apple is specifically doing about it in terms of notifying developers, banning access to the App Store for apps with the Mintegral SDK, or any other consequences.
I’ve contacted both Mintegral and Mobvista for comments, and will add their perspective or comments if and when they respond.
The Link LonkAugust 24, 2020 at 07:00PM
https://ift.tt/3l9mjCl
Malicious Chinese SDK In 1,200 iOS Apps With Billions Of Installs Causing ‘Major Privacy Concerns To Hundreds Of Millions Of Consumers’ - Forbes
https://ift.tt/2ZaIe2Q
iOS
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/22686894/backboneonexbox.jpg)
No comments:
Post a Comment